IBM Cognos Business Intelligence (BI) is a enterprise class, web-based, integrated business intelligence suite by IBM which provides toolset not only traditional BI capabilities like reporting, analysis, scorecarding, monitoring of events and metrics but also expands these capabilities with planning, scenario modeling, real-time monitoring, and predictive analytics. These capabilities deliver an easy-to-use and unified experience that is collaboration and social networking enabled. The
IBM Tivoli
Directory Server (TDS) is a
powerful and authoritative enterprise directory infrastructure that is a
critical enabler for enterprise security. It is an important part of the IBM
Security Integrated Identity Management portfolio. It plays a key role in
building the enterprise identity data infrastructure for applications such as
identity management, portals, and web services. It provides a server that
stores directory information using a DB2 database. It also provides a proxy
server for routing LDAP operations to directory servers with database. IBM
Security Directory Server provides client utilities and graphical user
interfaces (GUI), such as Instance Administration Tool (idsxinst) and
Configuration Tool (idsxcfg), to manage servers.
IBM Tivoli Directory
Server provides:
- Industry-standard architecture and broad platform
support for a range of
operating systems and applications and a variety of heterogeneous
environments.
- Strong scalability and flexibility to support hundreds of millions of entries using
IBM DB2 technology and a built-in proxy-server.
- Availability to support an identity data infrastructure for
global online applications such as consumer-driven web services.
- The ability to help you manage identities in the
cloud.
- Robust auditing and reporting that provides insight with connectivity to IBM
QRadar SIEM and greater visibility into repository with sample reports.
You can use IBM TDS to provide a
trusted identity data infrastructure for authentication. As we know Cognos BI
doesn’t provide its own authentication mechanism but leverage your existing
mechanism which you are using across enterprise applications. In this blog
article our objective is to leverage existing security features for
authentication and data transfer of TDS based LDAP with IBM Cognos BI to order
to secure BI assets and setup multi-tenancy environment.
This blog article describes
the step by step procedure for –
1)
Setting up TDS
6.2 environment on Windows 7 OS
2)
Integrating IBM
Cognos BI 10.2.1 Server with TDS 6.2.
3)
Enable
Multitenancy for Cognos BI environment
Also see –
Setting up TDS 6.2 Environment on Windows 7 OS
1)
Installation
steps are pretty easy and intuitive for TDS 6.2 by just double clicking
install_tds.exe file but if you are using later editions then you need to
install it thru IBM Installation Manager. Steps can be found here - http://publib.boulder.ibm.com/infocenter/tivihelp/v2r1/topic/com.ibm.IBMDS.doc_6.3.1/concept/c_ig_InstallationWithIBMInstallationManager.html
2)
On the
completion of installation, you can see ‘IBM Tivoli Directory …’ windows
services (Start->Programs->Administrative Tools->Services). The
default port used by TDS for LDAP service is 389.
3)
To create and
manage directory instances click on “Instance Administration Tool” from “IBM Tivoli
Directory Server 6.2” folder in Start Menu - > All Programs as shown in snapshot.
5)
We need to add “dc=example,dc=com” as a
new suffix before importing our example LDIF. After successful addition you
would see it in “Current suffix DNs” list.
6)
Below given is the
glimpse of sample LDIF, you can download the attachment (http://www.megafileupload.com/en/file/521432/IBM-TDS62-ldif.html) and change is as per
your requirements. I’ve created 11 users having userid admin, user1 – user10
with password – “password”. Lets click on “Import LDIF data”.
7)
Import sample
LDIF file.
8)
On successful
restoration start the server instance from “Manage Server
State
Integrating IBM Cognos 10.2.1 BI Server with TDS 6.2
It is assumed that Cognos 10.2 BI server is already installed and is in working condition. Open ‘IBM Cognos Configuration’ from Start -> All Programs -> IBM Cognos 10 – 64.
1)
In
the Explorer window, under Security, right-click Authentication, and then click New resource -> Namespace.
In the Name box, type a name for your authentication namespace (we used ‘IBM_TDS62’ here) and in the Type list, select ‘LDAP – Default values for IBM Tivoli’ and click OK.
2)
Select
the newly created namespace. In the ‘Resource Properties’ window in right, for the Namespace ID property, specify a unique
identifier for the namespace as TivoliLDAP is assigned in the below
screenshot. All entries with Red arrows are manually provided to integrate with
the TDS environment we created in above section.
If no values are specified, the LDAP authentication provider binds as anonymous.
If external identity mapping is enabled, Bind user DN
and password are used for all LDAP access. If external identity mapping is not
enabled, Bind user DN and password are used only when a search filter is
specified for the User lookup property.
4)
You can use user
attributes from TDS in namespace configuration. To configure this, you must map
these attributes with appropriate property name as shown in below snapshot. ‘Custom properties’ would be available as session
parameters through Framework Manager.
5)
From the File menu, click
Save. Test connectivity to the namespace
by right clicking on the name under Security, Authentication and selecting
test. If the test is successful, this message box will appear.
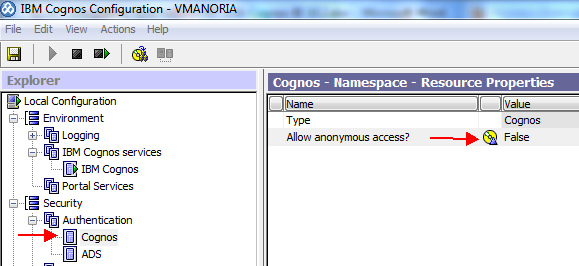
If you want to disable anonymous access, make sure you
disable it by setting ‘Allow anonymous access?’ property for ‘Cognos’ namespace
as shown below in snapshot.
7) Now anyone who wants to access Cognos
(http://localhost/ibmcognos), would be asked for authentication credential. Let
us login with LDAP administrator credential.
Directory
administrators would have Cognos admin privileges. Go to Cognos administration.
8) In ‘IBM Cognos Administration’, explore ‘Users,
Groups, and Roles’ under ‘Security’ tab. One can see the new
namespace (IBM_TDS62). Click on it to view all users belongs to the directory.
Administrator
now can assign different privileges and roles to these directory users as per
application security requirements by setting relevant properties. Once security
permissions are assigned, LDAP users are ready to use Cognos BI. For more
information on security, please refer to “IBM
Cognos BI Administration and Security Guide”.
Enable
Multitenancy for Cognos BI environment
1) We need to set multitenant properties from IBM Cognos Configuration tool to enable this feature. In IBM Cognos Configuration tool, select Security->Authentication->IBM_TDS62 in Explorer (left pane) window. Now select ‘Advanced Properties’ from right window (Resource properties) and add two new values before pressing OK button -
a)
Name – ‘multitenancy.TenantPattern’ value –
‘~/parameters/tenantID’
b)
Name – ‘AdditionalUserPropertiesToQuery’ value – ‘parameters’
2) Now, select ‘Custom Properties’ from right window (Resource properties) and add a new value –
Name – ‘tenantID’ value – ‘l’
3)
From the File menu, click Save. Test
connectivity to the namespace by right clicking on the name under Security,
Authentication and selecting test. If the test is successful, this message box
will appear.
4) Save
the configuration and restart Cognos service. Your Cognos multitenancy feature is
enabled.
There are many tasks follows this step to realize benefits of multitenancy in BI project. Please refer to my previous blog article http://vmanoria.blogspot.in/2014/03/ibm-cognos-bi-setting-up-multi-tenancy.html to see how to manage/administrate multi-tenant environment.
There are many tasks follows this step to realize benefits of multitenancy in BI project. Please refer to my previous blog article http://vmanoria.blogspot.in/2014/03/ibm-cognos-bi-setting-up-multi-tenancy.html to see how to manage/administrate multi-tenant environment.

























